Resin 3D printing, also known as vat photopolymerisation, is a rapidly growing additive manufacturing technology that produces high-quality, intricately detailed objects. This method utilises liquid photopolymer resins, which solidify or cure when exposed to a specific wavelength of light, creating layer-by-layer 3D structures.

Source: ZongHeng3D
Each step in the printing process plays a crucial role in ensuring that the final object matches the digital design accurately. Understanding how this technology works not only helps optimise prints but also troubleshoots common issues that may arise during printing.
How Resin 3D Printing Works
The process begins with a digital 3D model designed using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software. This model is then translated into a format readable by the 3D printer using slicing software, which divides the design into thin, horizontal layers.
The printing process typically involves these steps:
- Preparation: The resin tank is filled, and the build platform is positioned according to the object’s design.
- Layer Curing: The 3D printer selectively exposes specific areas of the liquid resin to light, following the sliced layers of the digital model. The exposed resin solidifies, forming the first layer of the object.
- Platform Movement: The build platform moves vertically, either up or down, depending on the printer’s design. This allows for a new layer of liquid resin to be exposed to the light source.
- Layer Repetition: These steps repeat, with the light source curing successive layers of resin based on the 3D model, until the entire object is formed.
Types of Resin 3D Printing Technologies
Resin 3D printing technologies have evolved significantly, offering users different methods for achieving their desired print quality and speed. Each type of technology brings its own set of advantages and trade-offs, depending on factors like resolution, build speed, and material usage.
Stereolithography (SLA)
Considered the first resin 3D printing technology, SLA utilises a UV laser to precisely trace and solidify each layer of liquid resin. SLA excels at producing parts with intricate details and smooth surface finishes but can be slower than other technologies as the laser draws each layer.
Digital Light Processing (DLP)
DLP printers employ a projector to cure an entire layer of resin simultaneously, significantly speeding up the printing process. While faster than SLA, the angled projection of light in DLP can sometimes lead to slight variations in pixel shape, potentially affecting accuracy in parts with highly complex geometries.
Masked Stereolithography (MSLA)
This variation of SLA uses a UV LED array and an LCD screen to control the light exposure for each layer. MSLA offers a balance of speed and detail, producing high-resolution parts at a faster rate than traditional SLA while mitigating the pixel distortion sometimes encountered in DLP.

Source: Kings3DPrinter
Advantages of Resin 3D Printing
The rise of resin 3D printing services has been driven by its numerous benefits, especially for industries requiring high detail and precision. It has carved a niche for itself due to the quality of the prints it delivers, making it a preferred choice for professionals and hobbyists alike.
High Resolution and Detail
Resin 3D printing allows for exceptionally fine details and smooth surface finishes, exceeding the capabilities of filament-based 3D printing (FDM) in creating intricate designs.
Speed
Particularly with DLP and MSLA, resin 3D printing can be significantly faster than FDM, as entire layers are cured simultaneously rather than tracing the design with a nozzle.
Material Variety
The market offers a wide array of resin materials with tailored properties, ranging from standard resins for general prototyping to specialised formulations for dental, high-temperature, or flexible applications.
Isotropy
Resin 3D printing results in objects with consistent strength in all directions due to the uniform curing process and the formation of covalent bonds between layers. This is crucial for functional parts requiring uniform strength and durability.
Watertightness
Resin-printed objects are inherently watertight, making them suitable for applications involving fluid control or containment.
Disadvantages of Resin 3D Printing
Despite its impressive capabilities, resin 3D printing isn’t without its challenges. Like any technology, it comes with certain limitations that may impact its usability for specific projects or users. Factors like post-processing requirements, material costs, and handling precautions can affect its overall appeal, especially when compared to other 3D printing methods.
- Smaller Build Volumes: Compared to FDM printers, resin 3D printers typically have smaller build areas, limiting the size of printable objects.
- Post-Processing Requirements: Resin 3D printing necessitates post-processing steps like washing to remove uncured resin, UV curing to completely solidify the object, and removal of support structures, adding time and effort to the process.
- Resin Shrinkage: The curing process can cause slight shrinkage in the resin, potentially leading to dimensional inaccuracies, especially in larger prints.
- Cost: While becoming more affordable, resin 3D printing generally involves higher upfront costs for printers and consumables like resin compared to FDM.
Safety Precautions: Handling resin requires caution as it can be an irritant or present health hazard. Proper ventilation, gloves, and eye protection are essential.
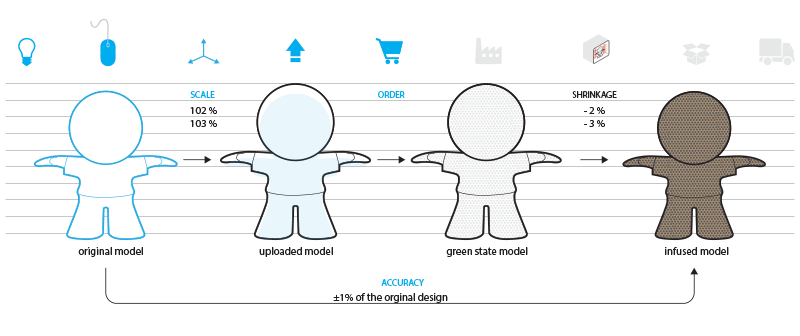
Source: i.Materlise
Applications of Resin 3D Printing
The versatility of resin 3D printing extends across a wide range of industries, from healthcare to creative arts. Its ability to produce highly detailed and accurate models makes it invaluable for applications that demand precision, such as dental work and jewellery design.
- Prototyping: Quickly create highly detailed prototypes to visualise designs and evaluate form, fit, and function early in the product development process.
- Jewellery Making: Produce intricate jewellery designs with castable resins for lost-wax casting or directly create master models for mould making.
- Dentistry: Fabricate dental models, surgical guides, retainers, aligners, and other dental appliances with precision and biocompatible materials.
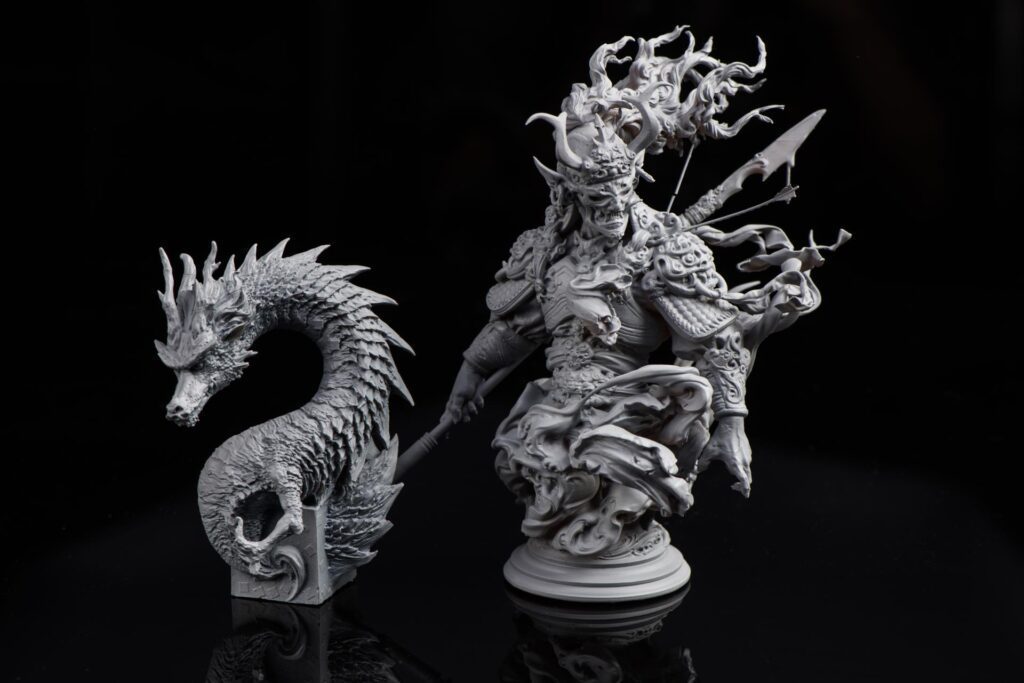
- Miniatures and Models: Create highly detailed miniatures and models for gaming, collecting, or educational purposes.
- Tooling: Produce moulds, jigs, and fixtures with high precision and dimensional accuracy for manufacturing processes.
Resin 3D Printing vs. Filament 3D Printing
Both technologies have strengths and weaknesses. While resin 3D printing offers unparalleled detail and surface finish, filament-based 3D printing remains a strong contender due to its affordability and ease of use.
- Resin 3D printing excels in: Detail, surface finish, speed, and the ability to produce isotropic and watertight parts.
- Filament 3D printing is generally: More affordable, offers a wider color palette, and is often considered more beginner-friendly.
Conclusion
Resin 3D printing offers a powerful manufacturing solution for producing high-quality, finely detailed parts with a wide range of applications. As technology advances, costs decrease, and material options expand, resin 3D printing will likely play an even more significant role in product development, manufacturing, and various industries.
For those looking to dive deeper into the world of 3D printing and explore its diverse technologies further, we have comprehensive guides available on SLA 3D printing and FDM 3D printing. Whether you’re a seasoned professional aiming to refine your technique or a beginner eager to understand the basics, these articles provide valuable insights and practical tips to help you maximize your 3D printing projects.
Discover the unique advantages and applications of each method by checking out our detailed articles on SLA and FDM 3D printing today!
