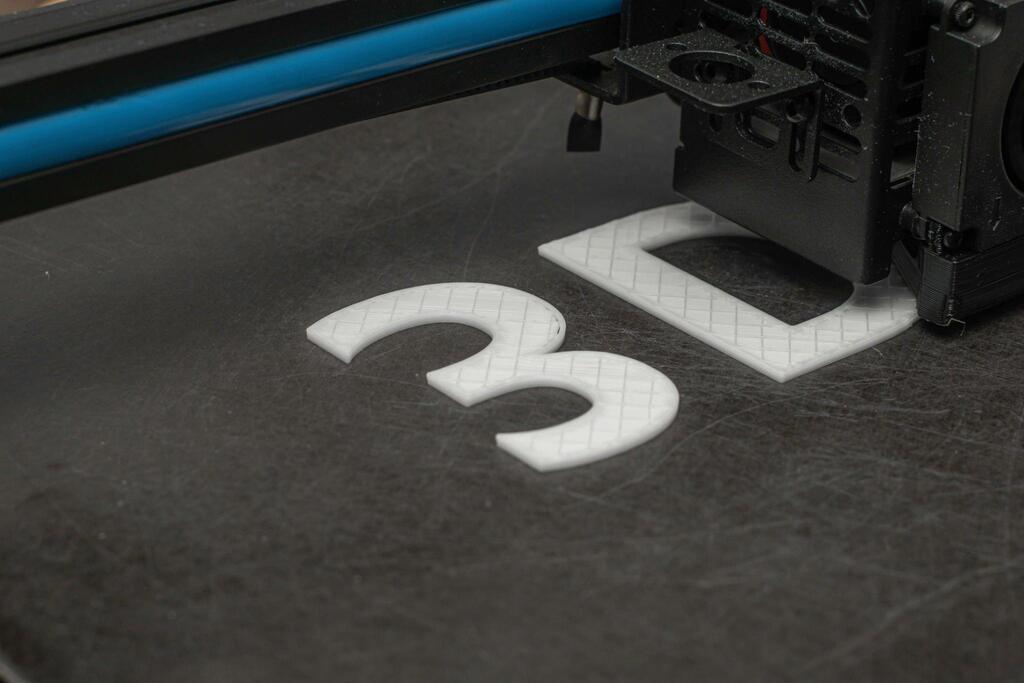
Malaysia is experiencing a remarkable transformation in the world of manufacturing, with the rapid advancement of 3D printing technology. Among the various 3D printing methods, Stereolithography (SLA) has emerged as a key player in shaping the future of this industry. SLA 3D print is a manufacturing technology that builds three dimensional objects layer by layer using a liquid photopolymer resin.
SLA is known for its high precision and surface quality, making it ideal for applications such as rapid prototyping, dental models and detailed prototypes. The choice of resin material is critical, as it impacts the final object’s properties, strength and durability. Choosing the right resin ensures the desired mechanical, chemical and aesthetic characteristics for the final printed part.
Types of Resins
Resin is the primary material used in SLA 3D print in Malaysia. It’s a specially formulated liquid compound consisting of photopolymers. The three common types of resins used in SLA 3D printing are: Standard resins, Engineering resins and Specialised resins.
Standard Resins:
Standard resins are the foundation upon which SLA 3D printing is built. They are versatile and offer a well-balanced blend of strength and detail. This versatility makes standard resins highly sought after for a range of applications.
Characteristics and Properties: They are known for their smooth surface finish, high-resolution printing capabilities and moderate strength. They are ideal for creating prototypes, intricate models and functional parts.
Common Applications in Malaysia: 3D printing shops widely use these resins across various sectors, including product design, architectural modelling, and creative arts. Their ability to produce intricate and finely detailed objects makes them a favorite among artists, designers, and engineers alike.
Engineering Resins:
Engineering resins are engineered for robustness and durability. They offer exceptional mechanical properties, making them suitable for applications where strength and reliability are paramount.
Strengths and Applications: In Malaysia, engineering resins find applications in creating functional prototypes, end-use parts, and components subjected to high stress. Industries such as automotive and manufacturing often rely on these resins for their toughness and resilience.
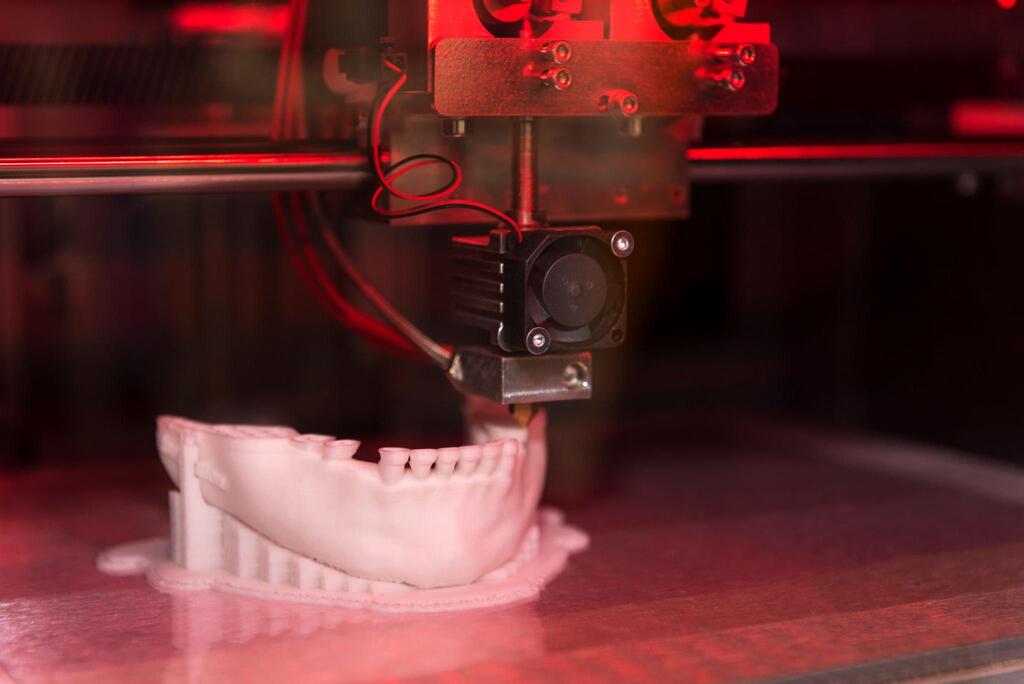

Specialized Resins:
Specialized resins cater to specific needs and requirements in Malaysia’s diverse industries. Two categories within specialized resins are biocompatible resins and high temperature resins.
Biocompatible Resins for Medical Applications: Malaysia’s healthcare sector has seen tremendous advancements with the introduction of biocompatible resins. These resins are designed to meet stringent safety standards and are used for producing medical devices, dental models, and prosthetics.
High Temperature Resins for Industrial Use: Malaysia’s industrial landscape requires materials that can withstand extreme heat and harsh environmental conditions. High temperature resins are tailor made for this purpose, finding applications in aerospace, automotive and various manufacturing processes.
Pros and Cons of SLA Materials
While SLA materials offer immense benefits, they are not without limitations. It’s essential to understand the pros and cons before selecting a material for a specific project.
Pros:
- High detail resolution.
- Smooth surface finish.
- Versatile applications.
- Enhanced strength and durability options.
Cons:
- Limited colour options compared to other 3D printing technologies.
- Some materials may be more brittle.
- Sensitivity to prolonged UV exposure in certain resins.
Photopolymerization Techniques
Photopolymerization is a fundamental process in the world of 3D printing, particularly in the context of SLA technology. It’s the magic that turns liquid resin into solid objects layer by layer. Understanding the various photopolymerization techniques is crucial for optimising 3D printing outcomes.
UV-Curing Resins: These resins solidify when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. They are prized for their precision and detailed resolution. UV-cured objects are perfect for jewelry, miniatures, and dental models. However, they may be sensitive to prolonged UV exposure and offer limited colour options.
DLP (Digital Light Processing) Resins: DLP employs a digital light projector to cure entire resin layers simultaneously. This results in faster printing times and is well-suited for creating larger objects. DLP resins are increasingly adopted in industries such as architecture, signage and dentistry.
Laser Based Resins: In this technique, a laser selectively cures the resin layer by layer, ensuring high precision and accuracy. It’s ideal for intricate mechanical parts and components. When choosing among these photopolymerization techniques, consider your project’s specific requirements for detail, size and material properties.

Factors Influencing Material Selection
Selecting the right material is a crucial decision in the world of 3D printing. Various factors come into play when determining the most suitable material for a particular project. The key factors that influence material selection in 3D printing:
Application and Use: The intended application of the 3D-printed object is a primary consideration. Different industries and projects require materials with specific properties, such as strength, flexibility or biocompatibility.
Material Properties: Each material has its unique set of properties, including strength, durability, thermal resistance and chemical resistance. Understanding these properties is essential to match them with project requirements.
Cost: Budget constraints often play a significant role in material selection. Some materials may be more cost-effective for a particular project, while others may be prohibitively expensive.

Conclusion
In conclusion, material selection is undeniably the linchpin in the world of SLA 3D printing, determining the quality, functionality and suitability of printed objects. It’s a meticulous process that can elevate or constrain the outcome of a project.
Considering Malaysia’s position in the global 3D printing landscape, it’s evident that the nation is rapidly emerging as a technological hub. The diverse range of materials available for SLA 3D printing in Malaysia, combined with the country’s innovative spirit, places it firmly on the map as a contributor to the ever-evolving world of additive manufacturing.

